Actually, it can. Solving the Einstein
field
equations
for an isotropic, homogeneous Universe yields a similar form for the
dynamics equation:


|
Actually, it can. Solving the Einstein
field
equations
for an isotropic, homogeneous Universe yields a similar form for the
dynamics equation:  which
is what we
had before, but with an additional
term called the "cosmological constant" expressing the effects of "dark
energy" (the vacuum energy density of space?). Solving this we get the
equation
governing the expansion of space:
|
 |
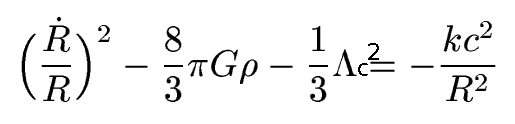 |
We can (and will!) solve this differential equation for different values of k and rho to get the detailed form of R(t).
First, though, two extended comments.
1. The meaning of rho.
We made the assumption of a matter dominated Universe (so that rho ~ R-3). This was not always true in the Universe. rho is actually the inertial mass density of the matter and radiation in the Universe. Remember that2. If Lambda is really a constant...and that So if we trace the history of the Universe back far enough, at some point the energy density of radiation exceeds that of matter, and we get to the radiation dominated era. At this point, the expansion dynamics are different, driven by radiation rather than gravity. This happens at a scale factor of R=10-3 - 10-4, so we can ignore it for the purposes of observational cosmology. But it does change the expansion rate in the early universe...
The energy density of matter and radiation drops as the universe expands. The density of dark energy does not. Eventually, Lambda wins. In this case, R ~ exp(t) -- exponential expansion.3. The complex interplay between expansion history and curvature
Without lambda, spatial curvature and expansion history were locked together. With lambda, that connection is broken. Closed universes can expand forever, open universes can collapse, etc. Life becomes messy!